Air Transport
General Cargo
Usually used for cargo that requires a very fast transit time such as perishable or pharmaceutical and also high value goods.
In order to calculate and air freight rate the following information is needed:
- Number of boxes / pallets / crates
- Dimensions and weight of each item
- Gross weight of the entire shipment (actual cargo plus the packing)
It’s really important that the weight and dimensions are correct as in air freight as there is a very specific way of calculating rates (this is called ‘chargeable weight’) based on the cargo weight / cargo dimension ratio.
Let’s explore an example of a chargeable weight calculation.
Pretend your consignment has a measurement of 200 cm (length), 160 cm (width), and 120 cm (height), and the gross weight of the shipment is 600 kg.
Here, volume = [200 x 160 x 120], meaning the volume is 3.84 cubic meters. Now, divide the answer (3,840,000) by 6,000 to get your volumetric weight of 640 kilograms.
So, the gross of 600 kilos is lower when compared to volumetric weight of 640 kilos. Therefore the airline will charge xxx USD per kilo based on 640 kilos.
We also need to know if the items can be stacked – so for example if you have a small carton or box can other cargo be placed on top of it. Generally, if cargo can be stacked the overall rate will be less.
Temperature controlled cargo
In the case that temperature control is required during the flight and at the airport cargo handling facilities at origin or destination, then the temperature regime is required, example -5 to –10 or +15 to +20 (degrees Celsius).
Hazardous cargo
While airlines do accept most types of hazardous cargo MSDS document will need to be provided before a quotation can be prepared.
The Material Safety Data Sheet is supplied by the manufacturer of the cargo and contains all the characteristics of the cargo and the hazardous elements therein.
If any items contain lithium batteries, then we need to know as there are very strict rules for this commodity and some airlines will not even accept. If items contain lithium batteries it is best, if possible, to send the cargo without them.
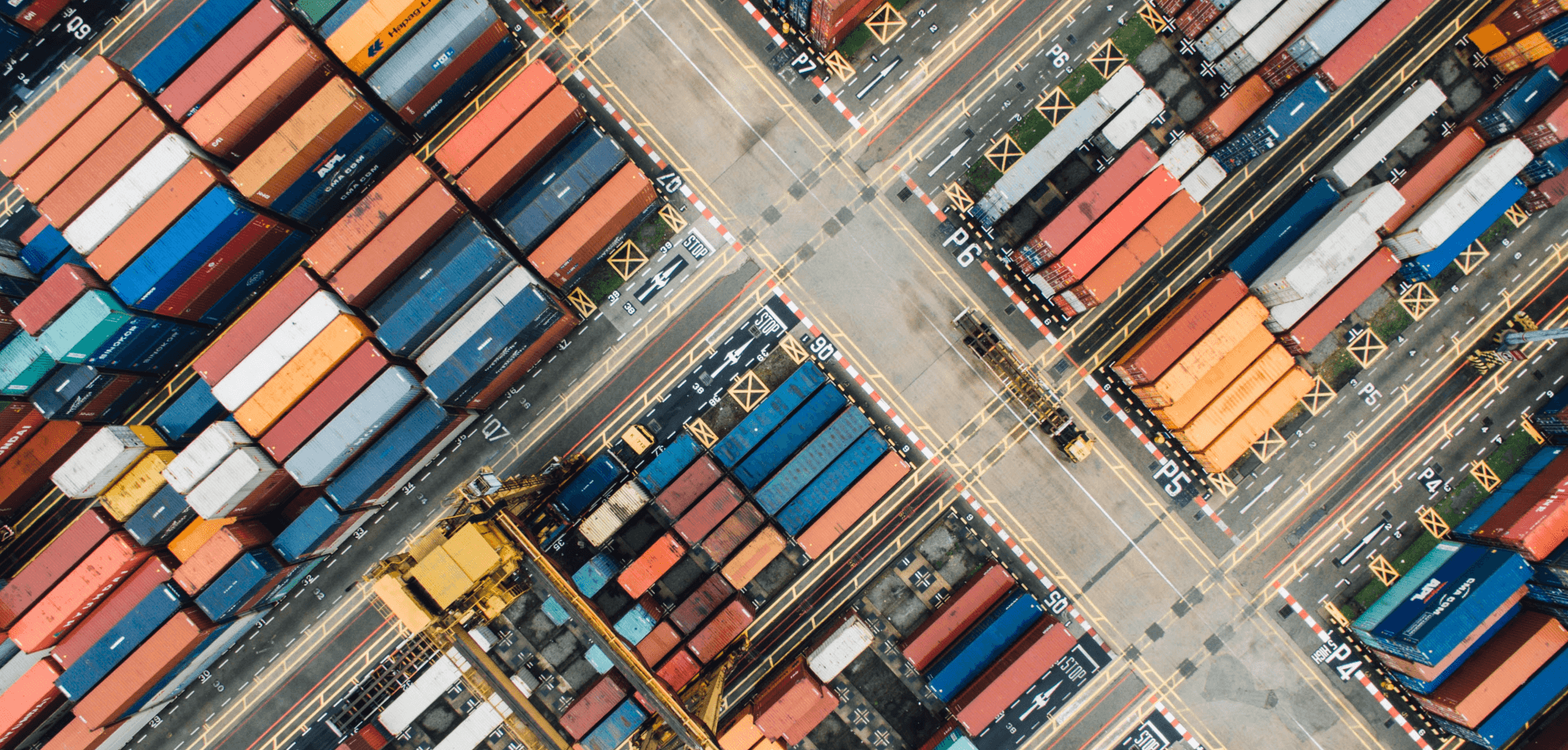
Ocean Transport
Most of global trade is conducted using ocean transport.
The type of ocean transport is dictated by the size of your shipment.
Let us start with FCL (Full Container Load) Shipping
FCL is used when you have enough cargo to fill an entire container. There are various types of containers and depending how much cargo you have will determine the size of the container. The three most popular container are: 20’ / 40’ and 40’ hight cube.
These are the internal dimensions – Length – Width – Height – in meters:
- 20’ 5.90 x 2.35 x 2.39
- 40’ 12.03 x 2.35 x 2.39
- 40’ high cube 12.03 x 2.35 x 2.70
In order to calculate an FCL rate the following information will be required:
- Commodity
- Gross weight of the entire shipment per container – so cargo plus outer packing
- MSDS document in some cases – see below
Some types of cargo (for example, liquids, sprays, ingredients, batteries, etc.) will require and MSDS – Master Data Safety Sheet.
The product must have a MSDS if, during or after use, the substance or material:
- changes its chemical composition;
- turns from solid to liquid, gas or vice versa;
- releases compounds into the environment that can harm health, property and the environment.
The Material Safety Data Sheet is supplied by the manufacturer of the cargo and contains all the characteristics of the cargo and the hazardous elements, if any.
The weight is very important as it can affect the haulage to and from the port, the actual ocean rate, as a rule 20 tons per 20’ or 40’ is OK, heavier weights can also be accepted but that can depend on the country the shipment is from and to.
If the cargo you need to move via FCL will not fit into a container then what we call special equipment is available.
The main types of special equipment are 20’ and 40’ open tops / 20’ and 40’ flat racks, 20’ and 40’ reefers.
Open tops:
Looks exactly like a standard container but has no roof so cargo what is high can fit into it, such as large machines.
These are the internal dimensions – Length – Width – in meters: 20’ 5.90 x 2.35 x 40’ 12.03 x 2.35
Flat racks:
A flat rack looks a container but has no sides or top. As such it can accommodate cargo that is wide and hight.
This is the length of a flat rack in meters: 20’ 5.9 / 40’ 11.65
In the case of any cargo that needs to be loaded into special equipment the following information is required:
- Total weight of the cargo including any outer packing
- Technical drawing of the cargo in question.
Reefers:
A reefer container is used when the cargo has to be shipped at a specific temperature, this can range from frozen meat to pharmaceuticals.
Before the cargo is loaded the reefer temperature is set to the required number of degrees.
The temperature will remain at the set number of degrees for the entire journey, so from the place of loading, during the ships voyage, and to the final delivery point.
These are the internal dimensions – Length – Width – Height – in meters: 20’ 5.45 x 2.29 x 2.16 40’ 11.59 x 2.29 x 2.40
In order to calculate a reefer freight rate then the following information will be required:
- Commodity
- Total gross weight of the cargo including any outer packing
- Required Celsius temperature
LCL shipment (Less than a Container Load)
LCL shipping will make most sense for your business when you need to transport smaller consignments via ocean sooner, rather than waiting for the moment when you’ll be able to fill a whole container. For LCL your cargo will move in a container with other cargo.
For LCL we can arrange collection of the cargo and move it to the LCL consolidation depot, this is the warehouse that the cargo is loaded into a container – after the container arrived at the deconsolidation warehouse at the final destination (this is the place the cargo is unloaded) arrangements can be made to move it to the consignee.
The following information will be required to calculate the rate:
- Commodity
- Dimensions of each piece
- Weight of each piece including outer packing
- Collection address unless the shipper delivers the cargo to the LCL consolidation warehouse
- Final delivery address unless the consignee will collect from the destination deconsolidation warehouse
Most LCL services only accept palletised cargo and usually nothing hazardous.
Rail Freight
The movements of cargo via rail can be considered for shipments from China to Russia and other countries where a rail link is available. Rail cargo provides a quick transit time, is ecologically friendly and for the most part is not interrupted by climatic conditions.
FCL via rail
As an example, FCL via rail from China to Russia. The container is positioned at the shippers facility for loading. After loading the container is taken to the nearest rail station. The container is then moved by rail to a Moscow rail station.
After arrival of the container it is sent to the final consignee.
In order to calculate the FCL rail rate we need the following information:
- Gross weight of the entire shipment per container – so cargo plus outer packing
- If the cargo is hazardous an MSDS document will need to be provided before a quotation can be prepared
The Material Safety Data Sheet is supplied by the manufacturer of the cargo and contains all the characteristics of the cargo and the hazardous elements therein.
The weight is very important as it can affect the haulage to and from the port, the actual ocean rate, as a rule 20 tons per 20’ or 40’ is OK, heavier weights can also be accepted but that can depend on the country the shipment is from and to.
LCL via rail
The shipment of LCL cargo is via rail is very similar to that of LCL via ocean. For LCL we can arrange collection of the cargo and move it to the LCL consolidation depot, this is the warehouse that the cargo is loaded into a container – after the container arrives at the destination railway station (this is the place the cargo is unloaded) arrangements can be made to move it to the consignees address.
The following information will be required to calculate the rate:
- Commodity
- Dimensions of each piece
- Weight of each piece including outer packing
- Collection address unless the shipper delivers the cargo to the LCL consolidation warehouse
- Final delivery address unless the consignee will collect from the destination railway station
Most LCL services only accept palletised cargo and usually nothing hazardous.
Transport by Road Vehicles
Transport via road can be used between countries that have a road link so for example Germany to Italy or even China to Russia and so on.
FTL (Full Truck Loads)
This is more or less the same of FCL via ocean and the same information is required. In order to calculate an FCL rate the following information will be required:
- Commodity
- Gross weight of the entire shipment per container – so cargo plus outer packing
- If the cargo is hazardous an MSDS document will need to be provided before a quotation can be prepared
The Material Safety Data Sheet is supplied by the manufacturer of the cargo and contains all the characteristics of the cargo and the hazardous elements therein.
As a rule 20 tons of total cargo is OK, heavier weights can also be accepted but that can depend on the country the shipment is from and to.
There are many types of road trailers and here are some of the ones available:
- Box Trailer: Length 13.62 m Width 2.46 Height 2.70 m
- Mega Trailer: Length 13.62 m Width 2.48 m Height 2.94 m
LTL (Less than a Truck Load)
Very similar to LCL via ocean freight. For LTL your cargo will move in a trailer with other cargo.
For LCL we can arrange collection of the cargo and move it to the LTL consolidation depot, this is the warehouse that the cargo is loaded into a trailer – after the trailer arrives at the deconsolidation warehouse at the final destination (this is the place the cargo is unloaded) arrangements can be made to move it to the consignee.
The following information will be required to calculate the rate:
- Commodity
- Dimensions of each piece
- Weight of each piece including outer packing
- Collection address unless the shipper delivers the cargo to the LTL consolidation warehouse
- Final delivery address unless the consignee will collect from the destination deconsolidation warehouse
Most LLT services only accept palletised / drums on pallets etc cargo and usually nothing hazardous.
Shipping Terms
For any type of commercial shipping via any mode of transport then there will be a contract between the seller and the buyer. Within this contract the terms of sale is mentioned. This is known as INCO TERMS International Chamber of Commerce and are standard for global commerce.
The INCO terms mentioned in the contract determine in terms of transport what the shipper and consignee are responsible for paying. These are the terms:
- EXW – Ex Works: The seller’s responsibility is to make the goods available for pickup at the warehouse or factory. From that point forward, the buyer assumes responsibility for all costs and risks.
- FCA – Free Carrier: The seller is responsible for delivering the goods to the carrier at a named place, which is usually the terminal or a warehouse. Once the goods are handed over to the carrier, the costs transfers to the buyer.
- CPT – Carriage Paid To: The seller is responsible for the costs of transporting the goods to a named destination. Responsibility transfers to the buyer once the goods are delivered to the agreed-upon destination.
- CIP – Carriage and Insurance Paid To: This incoterm is the same as CPT except that with CIP, the seller much also arrange and pay for insurance coverage in case of loss or damage to the goods during transit to the agreed-upon destination.
- DAP – Delivered at Place: The seller is responsible for arranging the entire shipment up to delivering the goods to a named place. Costs transfers to the buyer upon delivery. The seller is responsible for clearing goods for export but the buyer assumes responsibility for import customs duties, fees, and taxes.
- DPU – Delivered at Place Unloaded: The seller is responsible arranging the shipment and delivering the goods to a named place. They are also responsible for unloading them. Risk transfers to the buyer once the goods are unloaded.
- DDP – Delivered Duty Paid: The seller is responsible for entire shipment, including customs clearance and import tax and duty fees, and delivering the goods to the buyer’s premises. This incoterm places the maximum responsibility on the seller. Depending on the country of destianton DDP may or may not be available.
- FAS – Free Alongside Ship: The seller is responsible for picking up the goods at the factory, clearing them for export, and delivering them to a departure location, usually the ship loading dock. Costs transfers to the buyer when the goods are placed alongside the ship; they are responsible for the main leg of transit and every other step in delivery.
- FOB – Free On Board: The seller is responsible for packaging, pickup, and delivery of goods onto a vessel at the port of shipment. Costs transfers to the buyer once the goods are on board the vessel; the buyer is responsible for every other step of the journey.
- CFR – Cost and Freight: The seller is responsible for transportation to the port of origin and for loading the goods onto the vessel. They are also responsible for transportation to the destination port – but they are not liable for that portion of the journey. Instead, risk transfers to the buyer when the goods are on boarded at the origin port.
- CIF – Cost, Insurance, and Freight: Similar to CFR, but the seller also arranges and pays for insurance coverage for the goods during transit to the port of destination.
Customs Clearance
For every international freight movement customs clearance needs to take place. Customs clearance is the exercise of export customs clearing the cargo from the country of origin and at the country of destination.
Depending on the country of export then there may be a requirement to pay export tax and duty – this is based on the value and the commodity of the shipment. The same will apply when the cargo reaches the destination country.
Every country has its own rules which determine what, if any tax and duty has to be paid to the customs authorities.
Our team of experts can guide on this but will require the commodity HS Code and the value of the cargo.
What is an HS Code?
HS codes (Harmonized System codes), accepted by the majority of nations around the world, are identification codes given to goods for use in international trade. The HS codes are administered by the World Customs Organization (WCO) and are internationally accepted for use by customs authorities and companies to identify goods.
Key features of HS codes:
- Six digit code to classify the goods
- Defined rules that classify the goods
- Act as a uniform standard for classification of goods worldwide
- Covers 98% of goods in international trade and over 5000 commodities
Final Note:
As you can see there are many modes of transport available as well as other factors such as INCO terms that need to be considered when moving your cargo.
We hope the above guide will be of assistance but rest assured if you need any help then we are here!
 Cargo Transportation from Germany
Cargo Transportation from Germany
 Cargo Transportation from Taiwan
Cargo Transportation from Taiwan
 Cargo Transportation from Italy
Cargo Transportation from Italy
 Cargo Transportation from Indonesia
Cargo Transportation from Indonesia
 Cargo Transportation from Malaysia
Cargo Transportation from Malaysia
 Cargo Transportation from the UAE
Cargo Transportation from the UAE
 Cargo Transportation from Turkey
Cargo Transportation from Turkey
 Cargo Transportation from Russia
Cargo Transportation from Russia
 Cargo Transportation from China
Cargo Transportation from China
 Cargo Transportation from the USA
Cargo Transportation from the USA
 Cargo Transportation from India
All countries
Cargo Transportation from India
All countries
 Cargo Transportation from Germany
Cargo Transportation from Germany
 Cargo Transportation from Taiwan
Cargo Transportation from Taiwan
 Cargo Transportation from Italy
Cargo Transportation from Italy
 Cargo Transportation from Indonesia
Cargo Transportation from Indonesia
 Cargo Transportation from Malaysia
Cargo Transportation from Malaysia
 Cargo Transportation from the UAE
Cargo Transportation from the UAE
 Cargo Transportation from Turkey
Cargo Transportation from Turkey
 Cargo Transportation from Russia
Cargo Transportation from Russia
 Cargo Transportation from China
Cargo Transportation from China
 Cargo Transportation from the USA
Cargo Transportation from the USA
 Cargo Transportation from India
All countries
Cargo Transportation from India
All countries
 Cargo Transporation from Germany
Cargo Transporation from Germany
 Cargo Transporation from Taiwan
Cargo Transporation from Taiwan
 Cargo Transporation from Italy
Cargo Transporation from Italy
 Cargo Transporation from Indonesia
Cargo Transporation from Indonesia
 Cargo Transporation from Malaysia
Cargo Transporation from Malaysia
 Cargo Transporation from the UAE
Cargo Transporation from the UAE
 Cargo Transporation from Turkey
Cargo Transporation from Turkey
 Cargo Transporation from Russia
Cargo Transporation from Russia
 Cargo Transporation from China
Cargo Transporation from China
 Cargo Transporation from the USA
Cargo Transporation from the USA
 Cargo Transporation from India
All countries
Cargo Transporation from India
All countries